CONTENT
- Introduction & General Definition
- General Specifications of Diffractive Axicons
- Typical Applications
- Advantages of the Diffractive Axicon
- Principle of Operation and Design Considerations
- Diffractive Versus Refractive Comparison
- Comparison Between Binary and Multilevel Diffractive Axicon
- Sensitivity to Mechanical Tolerances
- Typical Optical Setups
- Diffractive Axicon Standard Products
- Diffractive Axicon Modeling Tutorial for Zemax
- Download PDF
INTRODUCTION
A Diffractive Axicon (DA) is a kind of Diffractive Optical Element (DOE) that transforms a laser beam into a ring shape (a Bessel intensity profile).
An Axicon also images a point source into a line along the optical axis and increases the Depth of Focus (DOF).
Each Diffractive Axicon lens is defined by its ring propagation angle. The calculated ring’s width (RW) is equal to ~1.75xDiffraction Limit (DLSM) at 1/e2 size of the input for Single Mode laser beam.
For multimode beam the Ring width will equal to:

Where:
EFL – effective focal length
λ – Wavelength
D – Input Beam Size
M2 – M2 value of input laser beam (beam quality)
Definitions of sizes for Diffractive Axicon:

General specifications of Diffractive Axicon LENSES
| Materials: | Fused Silica, Sapphire, ZnSe, Plastics |
| Wavelength range: | 193[nm] to 10.6[um] |
| DOE design: | Binary (2-level) and up to 16-levels |
| Diffraction efficiency: | 75% – 96% |
| Element size: | Few mm to 100[mm] |
| Damage threshold: | >3 [J/cm2] in 7 [nS] pulse @ 1064 [nm] |
| Coating (optional): | AR/AR Coating |
| Custom Design: | Almost any ring diameter |
Typical applications
| Atomic traps | Generating plasma in linear accelerators |
| Axicon resonators in lasers | Laser Corneal Surgery |
| Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) | Laser Drilling/Optical Trepanning |
| Telescopes | Solar concentrators |
Advantages of the Diffractive Axicon LENS
| Allows very small angles | Aberration free |
| Positive and negative configurations | Compact solution for larger angles – (fab. on thin window) |
| Exceptionally precise shape and angle | Plastic available for low power applications in low price |
| Fab. on Fused Silica or ZnSe (for infrared app.) | Arrays of micro Axicons |
| Can accept very small incident beams | |
| smaller loss caused by absorption in the material (especially in spectral ranges such as the UV, where absorption can be significant) | |
Principle of operation and design considerations
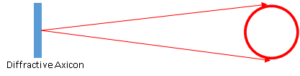 The principal of operation is similar as for basic focus lens.
The principal of operation is similar as for basic focus lens.
Unlike a Refractive Axicon (RA), which is defined with an apex angle or a cone angle, a Diffractive Axicon (DA) is defined by its divergence angle. The divergence angle defines ring diameter in specific distance.
The divergence angle ß (defined from peak to peak in intensity) can be calculated from the diffraction grating equation:
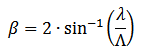
The ring diameter can be calculated from a geometrical point of view:
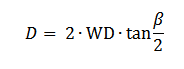
Where:
λ – Wavelength
Λ – Diffraction period
WD – Working distance
D – Ring Diameter
Example for finding the divergence angle:
- Wavelength: 355 [nm]
- EFL: 50 [mm]
- Desired Ring Diameter: 0.2 [mm]
![]()
Relation between Divergence Angle, and Cone Angle or Apex Angle of a Refractive Axicon:
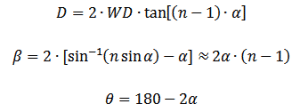
Where:
n – Refractive index
α – Base angle
θ – Apex angle
Another example for finding the divergence angle (β =?):
- Wavelength: 355 [nm]
- Cone angle: 0.25 [deg]
- Material Fused Silica
![]()
Diffractive versus Refractive comparison:
| Diffractive Axicon | Refractive Axicon |
| Function defined by divergence angle | Defined by cone or apex angle |
| Wavelength dependent | Polychromatic |
| No apex “dead” area | Has a “dead” area in the center |
| Accurately defined angle with no variation | Angle changes with production tolerances |
Comparison between binary and multilevel Diffractive Axicon:
A binary (or two levels) Diffractive Axicon lens can be an affordable alternative to a multilevel model or to a refractive element.
In the table below, we show simulation results corresponding to a specific example, with the following parameters:
- Wavelength: 1064 [nm]
- Beam diameter: 6 [mm]
- Laser: TEM00 Gaussian
- DOE clear aperture: 9.2 [mm]
- Ideal lens f=100 [mm]
Refractive or Multilevel Diffractive Axicon


Binary Diffractive Axicon


Superposition of profiles:

| Refractive or Multilevel Diffractive Axicon | Binary Diffractive Axicon | |
| Ring width (@1/e2) | ~1.75 x diffraction limit | ~ 1 x diffraction limit |
| Peak power | x 1.56 relative to multilevel | |
| Efficiency | 97.5 %(~100 % refractive) | 80 % (including side ring)* |
*Side ring vanishes for lasers with M^2 > 5.
Sensitivity to mechanical tolerances
| Tolerance | Value | Remark |
| Tilt X,Y | < 5 [deg] | Small amount of energy goes to Zero Order |
| Shift X,Y | Sensitive | Uniformity along ring |
| Tilt Z | No effect | |
| Shift Z | Yes | Depends on optical setup |
| Beam size | No Effect | |
| M2 | No Effect | |
| Polarization | No Effect |
Typical optical setups TBD
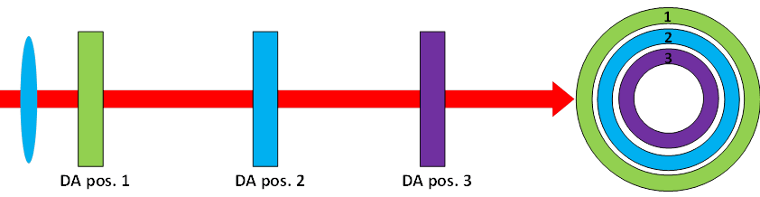
- Controlling ring width by placing Variable Beam Expander before Diffractive Axicon.
The diameter of the ring remains constant.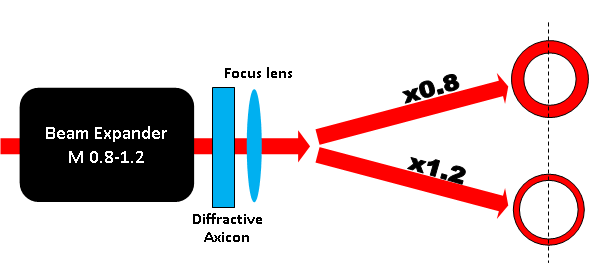
- Controlling Ring diameter by placing DA after focusing lens.
Ring diameter will reduce linearly with distance between diffractive pattern and image plane/ focal plane.
Ring width will remain constant.